The Lancet - excess heat deaths in Europe
-
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanplh/article/PIIS2542-5196(23)00023-2/fulltext
Background
Heat and cold are established environmental risk factors for human health. However, mapping the related health burden is a difficult task due to the complexity of the associations and the differences in vulnerability and demographic distributions. In this study, we did a comprehensive mortality impact assessment due to heat and cold in European urban areas, considering geographical differences and age-specific risks.
MethodsWe included urban areas across Europe between Jan 1, 2000, and Dec 12, 2019, using the Urban Audit dataset of Eurostat and adults aged 20 years and older living in these areas. Data were extracted from Eurostat, the Multi-country Multi-city Collaborative Research Network, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, and Copernicus. We applied a three-stage method to estimate risks of temperature continuously across the age and space dimensions, identifying patterns of vulnerability on the basis of city-specific characteristics and demographic structures. These risks were used to derive minimum mortality temperatures and related percentiles and raw and standardised excess mortality rates for heat and cold aggregated at various geographical levels.
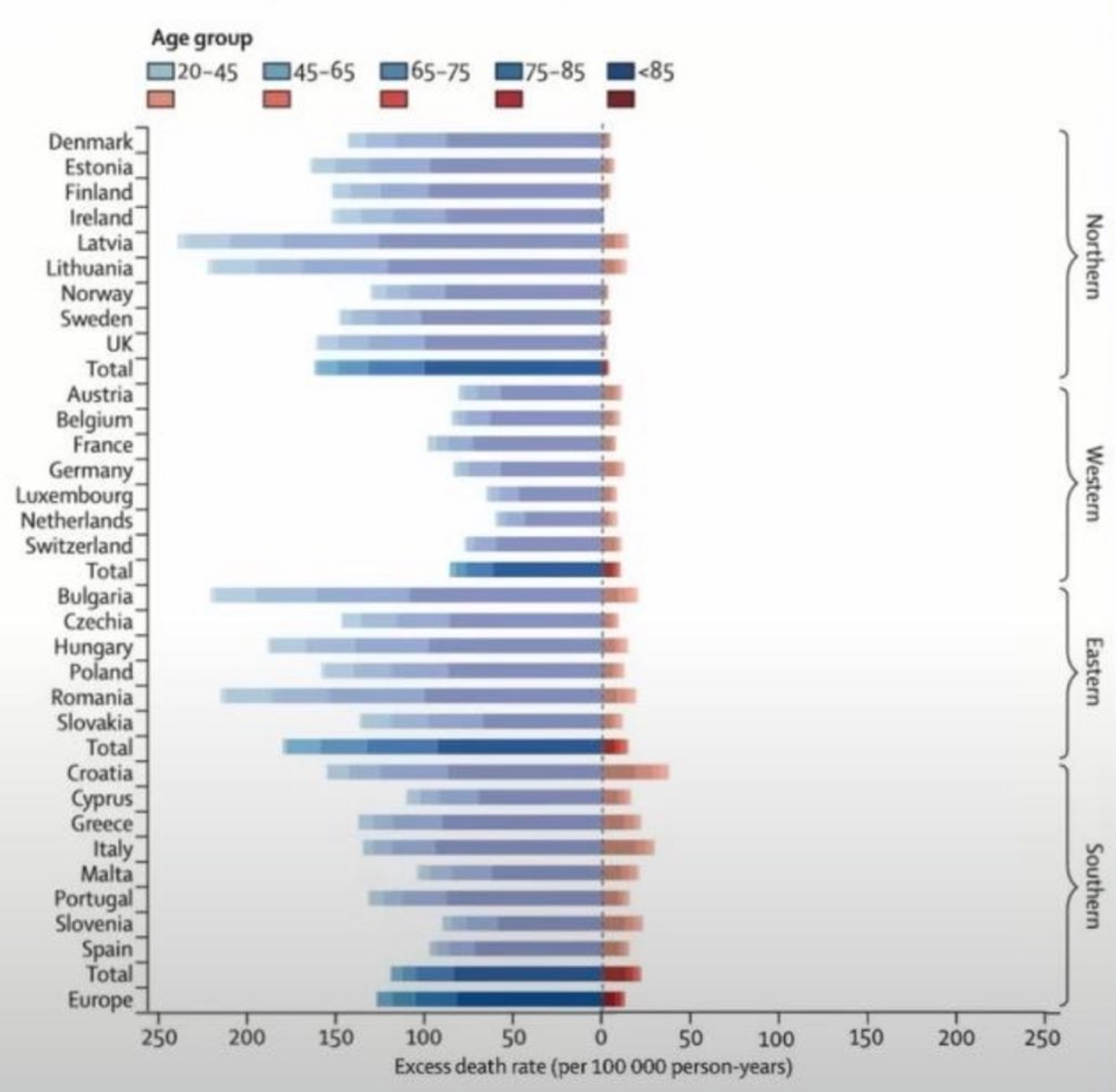
FindingsAcross the 854 urban areas in Europe, we estimated an annual excess of 203 620 (empirical 95% CI 180 882–224 613) deaths attributed to cold and 20 173 (17 261–22 934) attributed to heat. These corresponded to age-standardised rates of 129 (empirical 95% CI 114–142) and 13 (11–14) deaths per 100 000 person-years. Results differed across Europe and age groups, with the highest effects in eastern European cities for both cold and heat.
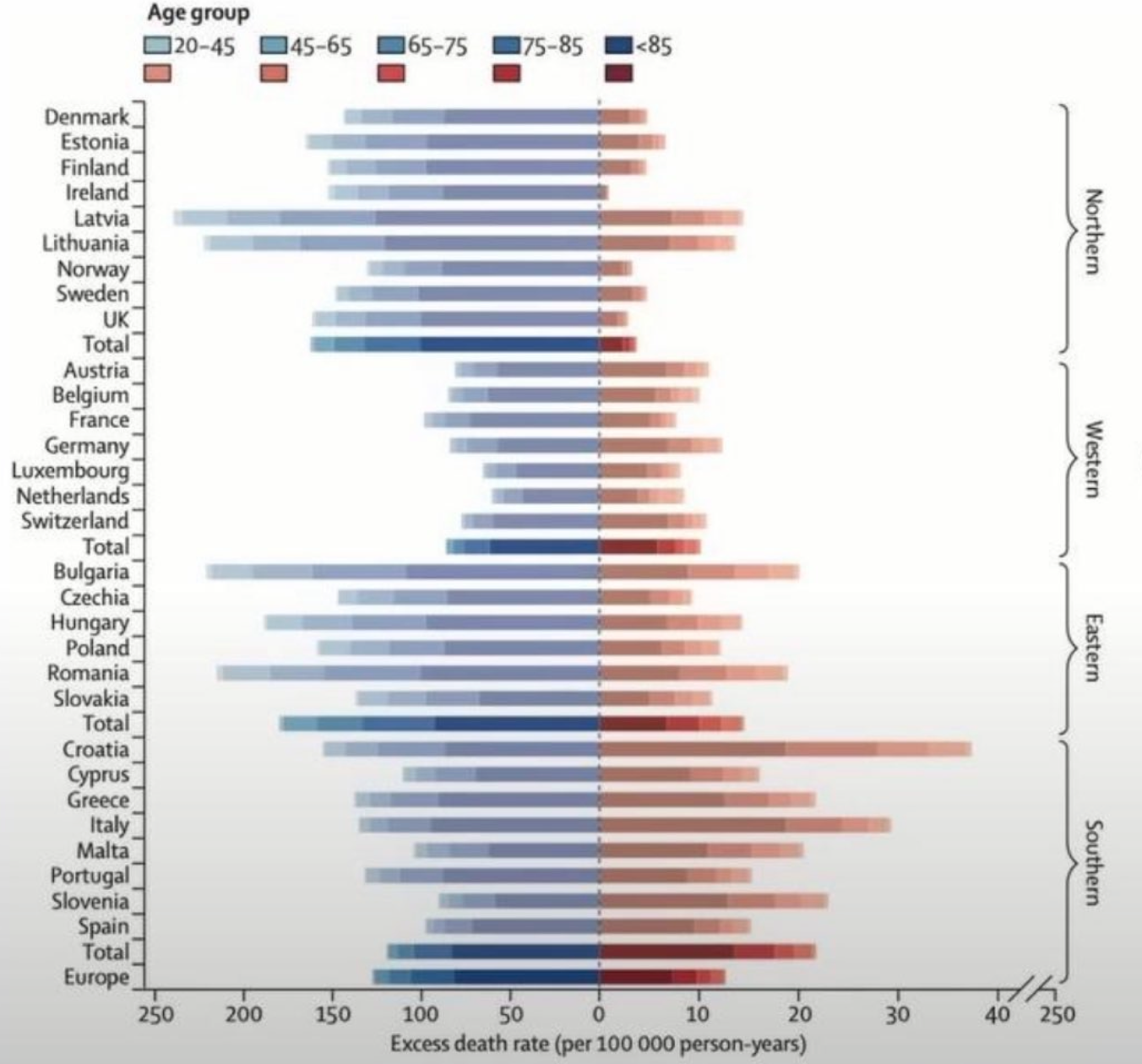
What does it look like if the axes on the bottom were the same scale...